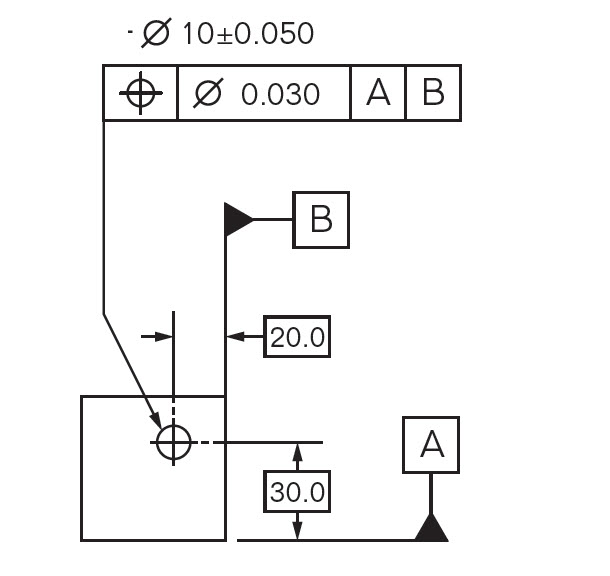
Dimensioning A Slot Pattern
Here's what it looks like. In response to Archie Manza: save such files to a file with the pattern name between the. and the, followed by.pat, e.g. For this one, SLOTPERF.PAT not case-sensitive, in a place in AutoCAD Support File Search Path list. Then use it in the Custom category in the Hatch dialog box. Same double-slit assembly (0.7 mm between slits); in top image, one slit is closed. In the single-slit image, a diffraction pattern (the faint spots on either side of the main band) forms due to the nonzero width of the slit. This diffraction pattern is also seen in the double-slit image, but with many smaller interference fringes. Directly dimensioning each of the positions within the pattern to each other may be acceptable in some scenarios, but likely isn’t a very clear choice for larger feature patterns. The problem with this scheme is that it can be very difficult to determine the true accumulation of the tolerance stack-up. The slot antenna was designed from the intuition of Babinet's principle, that a horizontal electric dipole in free space is the dual of a vertical slot and will have the same radiation pattern as. Within the Pattern command we are able to increment a feature through the spacing or size, we can control this using a dimension and even override individual instances. In this example we have a slot located on the origin and created a linear pattern going vertically above with 8 instances.
- Antenna Theory Tutorial
- Antenna Basic Terms
- Types of Antennas
- Antenna Arrays
- Wave Propagation
- Antenna Theory Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
A folded dipole is an antenna, with two conductors connected on both sides, and folded to form a cylindrical closed shape, to which feed is given at the center. The length of the dipole is half of the wavelength. Hence, it is called as half wave folded dipole antenna.
+Slots+are+dimensioned+by+their+diameters.jpg)
Frequency range
The range of frequency in which half wave folded dipole operates is around 3KHz to 300GHz. This is mostly used in television receivers.
Construction & Working of Half-wave Folded Dipole
This antenna is commonly used with the array type antennas to increase the feed resistance. The most commonly used one is with Yagi-Uda antenna. The following figure shows a half-wave folded dipole antenna.
This antenna uses an extra conducting element (a wire or a rod) when compared with previous dipole antenna. This is continued by placing few conducting elements in parallel, with insulation in-between, in array type of antennas.
The following figure explains the working of a half-wave folded dipole antenna, when it is provided with excitation.
If the diameter of the main conductor and the folded dipole are same, then there will be four folded (two times of squared one) increase in the feed impedance of the antenna. This increase in feed impedance is the main reason for the popular usage of this folded dipole antenna. Due of the twin-lead, the impedance will be around 300Ω.
Radiation Pattern
The radiation pattern of half-wave folded dipoles is the same as that of the half-wave dipole antennas. The following figure shows the radiation pattern of half-wave folded dipole antenna, which is Omni-directional pattern.
Half-wave folded dipole antennas are used where optimum power transfer is needed and where large impedances are needed.
This folded dipole is the main element in Yagi-Uda antenna. The following figure shows a Yagi-Uda antenna, which we will study later. The main element used here is this folded dipole, to which the antenna feed is given. This antenna has been used extensively for television reception over the last few decades.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of half-wave folded dipole antenna −
Reception of balanced signals.
Receives a particular signal from a band of frequencies without losing the quality.
A folded dipole maximizes the signal strength.
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of half-wave folded dipole antenna −
Displacement and adjustment of antenna is a hassle.
Outdoor management can be difficult when antenna size increases.
Applications
The following are the applications of half-wave folded dipole antenna −
Mainly used as a feeder element in Yagi antenna, Parabolic antenna, turnstile antenna, log periodic antenna, phased and reflector arrays, etc.
Generally used in radio receivers.
Most commonly used in TV receiver antennas.
PartDesign PolarPattern |
| Menu location |
|---|
| Part Design → PolarPattern |
| Workbenches |
| PartDesign |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| None |
|
Description
Dimensioning A Slot Pattern Block
The polar pattern tool takes a selected feature and creates a set of copies rotated around a chosen axis. Starting with v0.17, it can pattern multiple features.
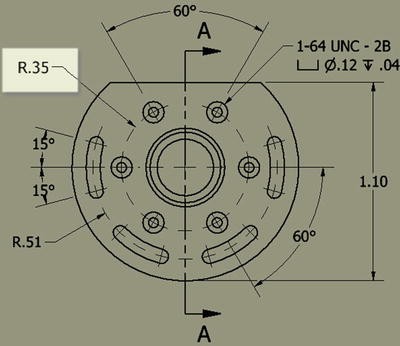
Above: a slot-shaped pocket (B) made on top of a base solid (A, also referred to as support) is used for a polar pattern. The result (C) is shown on the right.
Usage
To create a pattern:
- Select the feature (introduced in version 0.19 or several features) to be patterned.
- Press the PolarPattern button.
- Define the Axis. See Options.
- Define the Angle between the last copied occurrence and the original feature.
- Set the number of Occurrences.
- If you have several features in the pattern, their order can be important, see the image below. introduced in version 0.19 You can change the order by dragging the feature in the list and you will see the result immediately as preview.
- Press OK.
Effect of the feature order
To add or remove features from an existing pattern:
- Press Add feature to add a feature to be patterned. The feature must be visible in the 3D view:
- Switch to the Model tree;
- Select in the tree the feature to be added and press Spacebar to make it visible in the 3D view;
- Switch back to the Tasks panel;
- Select the feature in the 3D view; it will be added to the list.
- Repeat to add other features.
- Press Remove feature to remove a feature from the list, or right-click on the feature in the list and select Remove.
Options
Axis
When creating a polar pattern feature, the PolarPattern parameters dialogue offers different ways of specifying the pattern rotation axis.
Normal sketch axis
An axis being normal to the sketch and starting in the origin of the sketch of the feature being used is taken as axis for the polar pattern.
The pattern direction can be reversed by ticking 'Reverse direction'.
Horizontal sketch axis
Uses the horizontal axis of the sketch for axis.
Vertical sketch axis
Uses the vertical axis of the sketch for axis.
Custom Sketch Axis
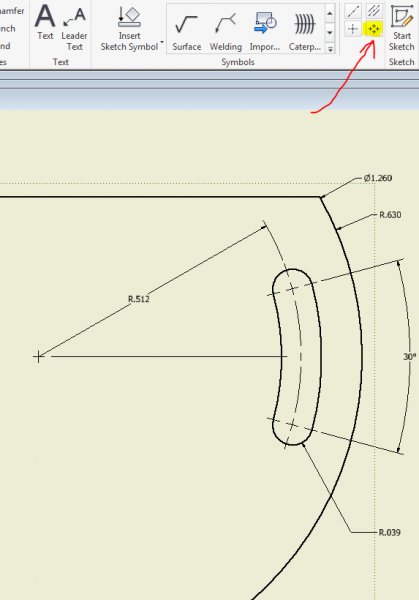
If the sketch which defines the feature to be patterned also contains a construction line (or lines), then the drop down list will contain one custom sketch axis for each construction line. The first construction line will be labelled Sketch axis 0.
Base (X/Y/Z) axis
v0.17 and above Select one of the Body Origin's standard axis (X, Y or Z) as axis.
Select reference...
Allows you to select either a DatumLine or an edge of an object or a line of a sketch to use for axis.
Angle and Occurrences
Specifies the angle to be covered by the pattern, and the total number of pattern shapes (including the original feature). For example, four occurrences in an angle of 180 degrees would give a spacing of 60 degrees between patterns. There is one exception: If the angle is 360 degrees, since first and last occurrence are identical, four occurrences will be spaced 90 degrees apart.
Limitations
- See linear pattern feature limitations.
- Structure tools:Std Part, Std Group
- Helper tools:Body, New sketch, Edit sketch, Map sketch
- Modeling tools
- Datum tools:Create a datum point, Create a datum line, Create a datum plane, Create a local coordinate system, Create a shape binder, Create a clone
- Additive tools:Pad, Revolution, Additive loft, Additive pipe, Additive box, Additive cone, Additive cylinder, Additive ellipsoid, Additive prism, Additive sphere, Additive torus, Additive wedge
- Subtractive tools:Pocket, Hole, Groove, Subtractive loft, Subtractive pipe, Subtractive box, Subtractive cone, Subtractive cylinder, Subtractive ellipsoid, Subtractive prism, Subtractive sphere, Subtractive torus, Subtractive wedge
Dimensioning A Slot Pattern Blocks
- Transformation tools:Mirrored, Linear Pattern, Polar Pattern, Create MultiTransform
- Dress-up tools:Fillet, Chamfer, Draft, Thickness
- Boolean:Boolean operation
- Extras:Migrate, Shaft design wizard, Involute gear
- Contextual Menu tools:Set tip, Move object to other body, Move object after other object
Dimensioning A Slot Pattern Tool
- Installation:Download, Linux, Windows, MacOS, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics:About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties; Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help:Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches:Std Base; Arch, Draft, FEM, Image, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Path, Points, Raytracing, Reverse Engineering, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Unmaintained workbenches:Plot, Robot, Ship
- Deprecated workbenches:Complete, Drawing
- Code:Addon Manager, Addons, Macros, External workbenches
- Hubs:User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub